Fatty Acid Methyl Esters; A Component of Biodiesel Made From Recycled Cooking Oils and Plant Based Material
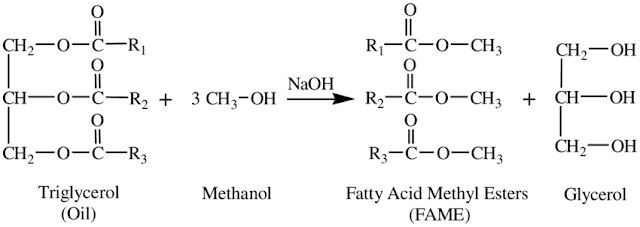
Fatty acid methyl esters are a type of fatty acid ester that are derived by transesterification of fats with methanol. The molecules in biodiesel are primarily fatty acid methyl esters, obtained from vegetable oils by transesterification. They are used to produce biodiesel and detergents. They are produced from animal fats, vegetable oils, or waste cooking oils by transesterification. In the transesterification process a glyceride reacts with an alcohol in the presence of a catalyst, forming a mixture of fatty acids esters and alcohol. FAME (fatty acid methyl ester) is a generic chemical term for biodiesel derived from renewable sources. They are used to extend/replace mineral diesel and gas oil used to fuel on and off-road vehicles and static engines.
Fatty
Acid Methyl Esters is a key component of biodiesel. It is obtained from
vegetable oils and is used in biodiesel and detergents. They are not a
substitute for biodiesel, but can be used in their place. Fatty acid methyl
esters are typically produced by converting the free fatty acids in an acid fat
or oil to a corresponding methyl ester. To perform this procedure, a small
amount of methanol is added to the acid fat or oil, followed by the addition of
a catalyst. The reaction mixture is then subjected to conditions that will make
FAME form. Fatty acid methyl esters are also easily separated from their parent
triglycerides and can be quantified with GC-MS. These fatty acids are the key
to biodiesel production.
In
biodiesel, they are the main constituents. These fatty acids are derived from
vegetable oils through the process of transesterification. The resulting
biodiesel molecules are very soluble in organic solvents, making FAME an
excellent substitute for fossil fuels. They also have many other uses, including
lubricants, detergents, agriculture, and surfactants. To make FAME, the
reaction is completed in 20 minutes at a concentration of 1.2% HCl. This
reaction was repeated at lower HCl concentrations. The resulting FAMEs were
analyzed using a gas chromatograph with a SUPELCOWAX 10 column. The final
concentration of HCl was 1.2% w/v. If there is a methylation reaction, a FAME
is produced.
The
composition of fatty acid methyl esters depends on the type of alcohol used to
convert the fatty acid to its fatty acid ester form. They are produced as
monoglycerides, diglycerides, and triglycerides. The properties of biodiesel
are influenced by the fatty acid methyl esters. The fatty acid methyl esters
also differ in their molecular structure and chain length. FAMEs (fatty acid
methyl esters) analysis is an important tool both for characterizing fats and
oils and for determining the total fat content in foods. Fats can be extracted
from a matrix using a nonpolar solvent and saponified to produce salts of the
free fatty acids. The use of FAME as biomarkers to identify groups of
microorganisms was studied.
The
most widely accessible biodiesel type in the marine industry is fatty acid
methyl esters-based biofuel, which is typically blended with regular marine
diesel. FAME's also used as a thickening & emulsifying agent in the
food industry. Fatty acid methyl esters are also used in the personal care
& cosmetics industry.



Comments
Post a Comment