Recombinant DNA Technology; an Effective Way of Producing Proteins
Recombinant DNA Technology is a method of genetically engineering an organism or its product by introducing and integrating genetic material from other species into the genome of an existing one. This alteration can be made to enhance an existing trait or produce a new one. It also can be used for the development of novel proteins or therapeutic compounds.
Recombinant
genes are produced by the use of different laboratory techniques to put a small
fragment of DNA into a cell or an organism, such as a bacteria, yeast, or
fungus, where it will copy itself along with its own DNA. This allows
scientists to study the structure, function, and expression of genes, as well
as explore many questions related to the biology of a living organism.
Recombinant
DNA Technology method has been extremely
effective in producing important proteins, including insulin and growth
hormone, for treating diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and hereditary disorders.
It also has been used to introduce genes that make crops resistant to weeds and
insects, which reduces the cost of pesticides by farmers and improves
agricultural yields.
Several
steps are involved in the recombinant DNA technology process, and each step has
a specific purpose. First, the DNA of interest is isolated and then it is
modified using enzymatic cleavage with restriction enzymes to obtain the
desired DNA fragments. These fragments are then joined together using ligase
activity to produce the desired gene.
The
genetic material is then inserted into the vector which is a small replicating
molecule that carries the desired DNA. There are different types of vectors
used in recombinant DNA technology, such as plasmids, bacteriophages, and viruses.
Plasmids
are the most common vectors in recombinant DNA technology. They contain an
origin of replication, a selectable marker and cloning sites. The restriction
enzymes will recognize these cloning sites and the recombinant DNAs are then
inserted into them.
Bacteria
and yeast are also commonly used in recombinant DNA technology. These organisms
have simple genetic machinery, and thus are very suitable to carry out the
recombinant DNA technology process. These organisms can be engineered to
produce a particular protein, such as insulin, or a gene that produces an
immune system response. They are also useful for creating microbial strains
that can be used as factories to produce recombinant drugs.
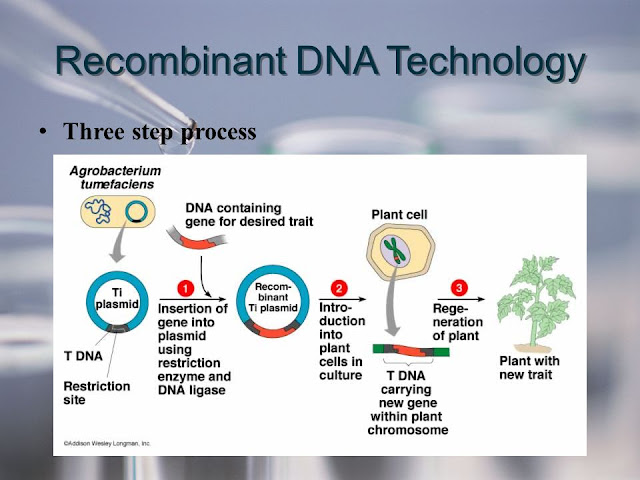
Plants
are also commonly used in recombinant genetic technology. They can be
genetically engineered to produce certain proteins, such as insect-killing
toxins that disrupt the gut function of insect larvae that are the main food
source of crop pests. Recently in March 2022, VBI Vaccines Inc. introduced
PreHevbrio, a recombinant vaccines for Hepatitis B, in the U.S. to prevent
infection in adults.



Comments
Post a Comment