The Role of Flow Cytometry in Stem Cell Research: Characterizing and Isolating Stem Cell Populations
Flow Cytometry has emerged as an invaluable tool in stem cell research, enabling scientists to characterize and isolate specific populations of stem cells with unprecedented precision. Stem cells, known for their remarkable regenerative capabilities and potential to differentiate into various cell types, hold great promise for regenerative medicine and understanding human development. Flow cytometry offers a comprehensive and efficient approach to analyze and separate stem cell populations based on their unique surface markers and functional properties.
Characterizing stem
cell populations is a crucial step in stem cell research, as it helps
scientists understand their heterogeneity, functionality, and potential
applications. allows researchers to identify and quantify specific cell surface
markers associated with stem cells using fluorescently labeled antibodies. By
analyzing the expression patterns of these markers, scientists can distinguish
different types of stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells, induced
pluripotent stem cells, and various adult stem cell populations. This
information is vital for studying the developmental processes of stem cells and
evaluating their therapeutic potential.
Flow
Cytometry enables researchers to assess the
functional properties of stem cells. For example, using fluorescent dyes and
probes, flow cytometry can measure the metabolic activity, viability, and
proliferation rates of stem cells. It can also evaluate the differentiation
potential of stem cells by assessing their ability to give rise to different
cell lineages. By combining these functional analyses with surface marker
characterization, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the behavior
and regenerative capacity of stem cells.
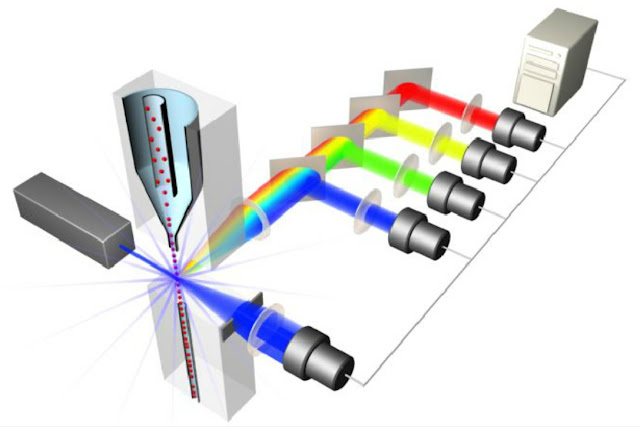
In addition to
characterization plays a pivotal role in isolating specific populations of stem
cells. This technique utilizes the principle of fluorescence-activated cell
sorting (FACS), where cells are labeled with fluorescent tags and sorted based
on their unique characteristics. By setting specific gating parameters,
researchers can isolate stem cell populations of interest from complex mixtures
of cells. This allows for the purification of homogeneous stem cell populations
for further downstream experiments or therapeutic applications.
The ability to isolate
stem cell populations using flow cytometry has revolutionized the field of
regenerative medicine. Researchers can obtain highly pure stem cell populations
for transplantation, tissue engineering, and cell-based therapies. Furthermore,
isolated stem cell populations can be utilized to study their gene expression
profiles, epigenetic modifications, and molecular signatures, providing crucial
insights into the underlying mechanisms of stem cell function and
differentiation.
Flow
Cytometry has become an indispensable tool in stem
cell research, facilitating the characterization and isolation of specific stem
cell populations. Through the analysis of surface markers and functional
properties, provides valuable information about stem cell heterogeneity and
functionality. Moreover, the ability to isolate pure stem cell populations has
opened new avenues for regenerative medicine and advanced our understanding of
stem cell biology. As technology continues to advance, will undoubtedly play an
even more significant role in unraveling the mysteries of stem cells and their
therapeutic potential.



Comments
Post a Comment