Understanding The Impact Of Social Determinants Of Health
 |
| Social Determinants Of Health |
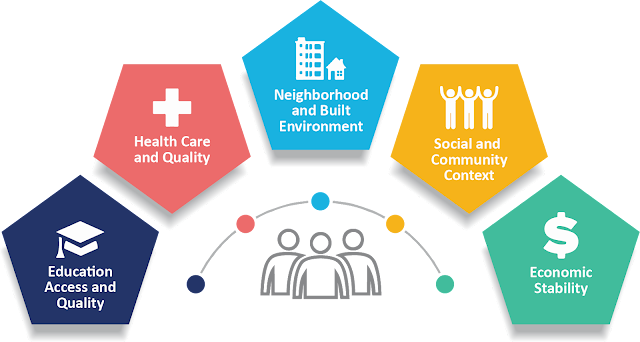
In recent years, there has been growing recognition of the significant role that social determinants of health play in shaping individual and population health outcomes. Social determinants of health refer to the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age, as well as the wider set of forces and systems shaping the conditions of daily life. These factors, which include socioeconomic status, education, employment, housing, and access to healthcare, have a profound impact on health disparities and inequalities. In this article, we'll explore the concept of social determinants of health, their impact on health outcomes, and strategies for addressing health inequities.
1. Socioeconomic
Status:
One of the most
significant Social
Determinants Of Health is socioeconomic status, which encompasses
factors such as income, education, and occupation. Individuals with higher
socioeconomic status tend to have better access to resources such as quality
healthcare, nutritious food, safe housing, and education, leading to improved
health outcomes. Conversely, those with lower socioeconomic status are more
likely to experience barriers to healthcare access, higher rates of chronic
disease, and increased mortality rates.
2. Education:
Education plays a
crucial role in shaping health outcomes, as it influences employment
opportunities, income levels, and access to information and resources.
Individuals with higher levels of education are more likely to engage in
health-promoting behaviors, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and
preventive healthcare. Additionally, education is linked to better cognitive
function, mental health, and overall well-being, contributing to lower rates of
chronic disease and disability.
3. Employment and
Working Conditions:
Employment status and
working conditions also have a significant impact on health outcomes. Stable
employment provides individuals with income security, access to
employer-sponsored healthcare, and opportunities for personal and professional
development. Conversely, precarious employment, low wages, and unsafe working
conditions can lead to stress, anxiety, and poor health outcomes. Additionally,
occupational hazards such as exposure to toxins, physical injury, and workplace
stress can contribute to the development of chronic diseases and disabilities.
4. Housing and
Neighborhood Environment:
The quality of housing
and the neighborhood environment are important determinants of health,
influencing factors such as safety, access to green spaces, and exposure to
environmental toxins. Individuals living in unsafe or overcrowded housing
conditions are at higher risk of injury, infectious diseases, and mental health
problems. Additionally, neighborhoods with limited access to healthy food
options, recreational facilities, and healthcare services can contribute to
disparities in health outcomes.
5. Access to
Healthcare:
Access to healthcare
services is a critical social determinant of health, as it directly impacts
individuals' ability to receive timely and appropriate medical care. Barriers
to healthcare access, such as lack of health insurance, transportation, and
language barriers, can prevent individuals from seeking preventive care,
managing chronic conditions, and accessing emergency services. Addressing
disparities in healthcare access is essential for improving health outcomes and
reducing health inequities.
6. Strategies for
Addressing Health Inequities:
Addressing health
inequities requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying
social determinants of health. This includes implementing policies and programs
that promote economic stability, improve educational opportunities, create safe
and supportive environments, and expand access to healthcare services.
Additionally, efforts to address structural racism, discrimination, and social
exclusion are essential for achieving health equity and ensuring that all
individuals have the opportunity to attain their highest level of health.
Social determinants of
health play a significant role in shaping individual and population health
outcomes, contributing to health disparities and inequities. Understanding the
impact of social determinants of health is essential for developing effective
strategies to promote health equity and improve health outcomes for all. By
addressing the underlying social and economic factors that influence health, we
can create a more just and equitable society where everyone has the opportunity
to thrive.



Comments
Post a Comment